
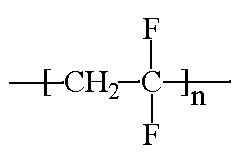
ACRONYMS, TRADE NAMES: PVDF, PVF2, Kynar, Solef, Neoflon, Foraflon, KF, Soltex
CLASS: Vinylidene polymers
Poly(vinylidene fluoride), or PVDF, has a few things going for it. It has very high electrical resistance, and it has good flame resistance. Put these two bits of information together and it might dawn on you that this would make a good material for insulating electrical wires, especially ones that get hot during use. So you"ll find it insulating the wires in the computer you"re using right now. Electrical cables on airplanes are also insulated with PVDF, where it"s important that practically everything on board be fireproof. It"s also chemically resistant, so you"ll find it used in the chemical industry to make pipes and bottles and such that hold chemicals. What about ultraviolet radiation? PVDF resists that, too. PVDF is often blended with poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) to make it more resistant to UV light. PMMA degrades when exposed to UV radiation, so if we want to make PMMA windows for use outside we have to blend it with PVDF.
Another nifty thing about PVDF is that it"s a piezoelectric material. What does that mean? That means that when it"s placed in an electric field it changes its shape.
Because fluorine is so much more electronegative than carbon, the fluorine atoms will pull electrons away from the carbon atoms to which they are attached. This means the -CF2- groups in the chain will be very polar, with a partial negative charge on the fluorine atoms and a partial positive charge on the carbon atoms. So when they"re placed in an electrical field, they align. This causes the polymer sample to deform, all those -CF2- groups trying to align.
Now here"s the fun part:
If you put it in an alternating electrical field it"ll vibrate, deforming in one direction, and then in the opposite direction. This vibration can be used to produce sound. This is how piezoelectric tweeters work.
PVDF is made by free radical vinyl polymerization of the monomer vinylidene fluoride, like this:
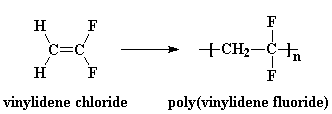
PropertiesGlass transition temperature: -38oC. Melting temperature: 160oC. Amorphous density at 25oC: 1.74 g/cm3. Crystalline density at 25oC: 2.00 g/cm3. Molecular weight of repeat unit: 64.03 g/mol.
MAJOR APPLICATIONS:Wire and cable insulation, tubing, piping, sheet and melt-cast®lms for electrical and electronics, binder for high-quality metal ®nishes for uilding components used on exterior wall panels, roo®ng shingles, and on industrial, commercial and residential buildings, used in fluid handling systems for solid and lined pipes, ®ttings, valves, and pumps, in manufacture of microporous and ultra®ltration membranes, chemical-tank lining, telephone headset, infrared sensing, hydrophones, keyboards and, printers. PROPERTIES OF SPECIAL INTEREST:Excellent mechanical properties and resistance to severe environmental stress, good chemical resistance, good piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties PREPARATIVE TECHNIQUES Emulsion polymerization: (a) 300±800 psig, perfluorinated surfactant initiator, 65±858C, 2±6 h; (b) 200 lb in2, 50±1108C, fluorinated surfactant, 17±21 h, iron powder. Suspension polymerization: suspending agent, reaction accelerator, water soluble initiator, 300±1,000 psig, 35±1008C.
click this for Typical physical properties references of this text are : 2- http://www.polymerprocessing.com/ 3- Polymer Data Handbook. Copyright # 1999 by Oxford University Press, Inc. All rights reserved. |




